
Internationalization in MLM software means building platforms that can seamlessly adapt to global markets by supporting multiple currencies, languages, tax profiles, and region-specific catalogs and fulfillment rules. It ensures distributors and customers across different countries can transact, communicate, and comply with local regulations without friction—making it a critical driver for MLM companies aiming to expand and compete internationally.
The multi-level marketing (MLM) industry has become a $68.3 billion global business in 2024 (WFDSA Global Statistics, 2024). Companies like Amway, Herbalife, and Avon have established networks spanning over 100 countries. But behind the scenes, their success depends not just on product appeal but also on the internationalization of MLM software—the backbone that manages distributors, transactions, taxation, logistics, and compliance across diverse markets.
Internationalization in MLM software means making platforms adaptive to local currencies, languages, tax systems, product catalogs, and fulfillment rules without compromising central control. Let’s break down the two critical pillars that define this transformation.
In 2025, cross-border e-commerce accounts for 22% of global online sales (Statista, 2025). MLM distributors increasingly operate internationally, demanding payment systems that can handle USD, EUR, JPY, INR, and crypto wallets simultaneously.
According to CSA Research (2023), 76% of global buyers prefer purchasing in their native language. MLM software must therefore support multilingual interfaces not only for customers but also for back-office dashboards.
This not only improves adoption but also compliance with consumer protection laws in regions where language clarity is mandated.
Taxation is the trickiest layer of internationalization. With the OECD reporting $150B lost annually in global tax evasion (2023), governments are tightening cross-border rules. MLM companies must comply with:
For MLM companies, failing tax compliance doesn’t just mean penalties—it risks losing licenses to operate.
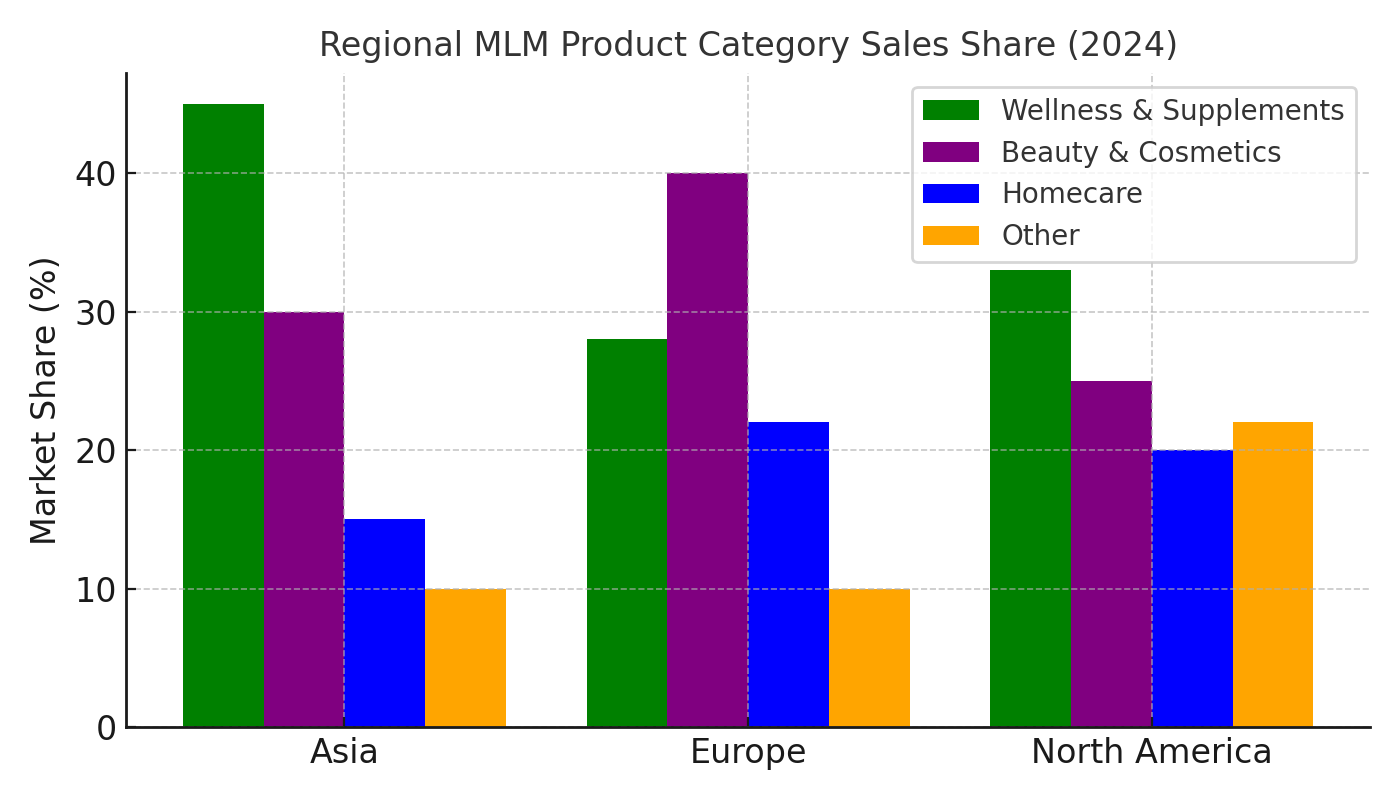
Not every product can be sold in every country. For example:
MLM software enables regional catalogs:
Logistics determine customer satisfaction in international MLM. In fact, Deloitte’s Global Supply Chain Survey (2024) shows 58% of cross-border e-commerce complaints stem from delivery delays and costs.
MLM software manages fulfillment by:
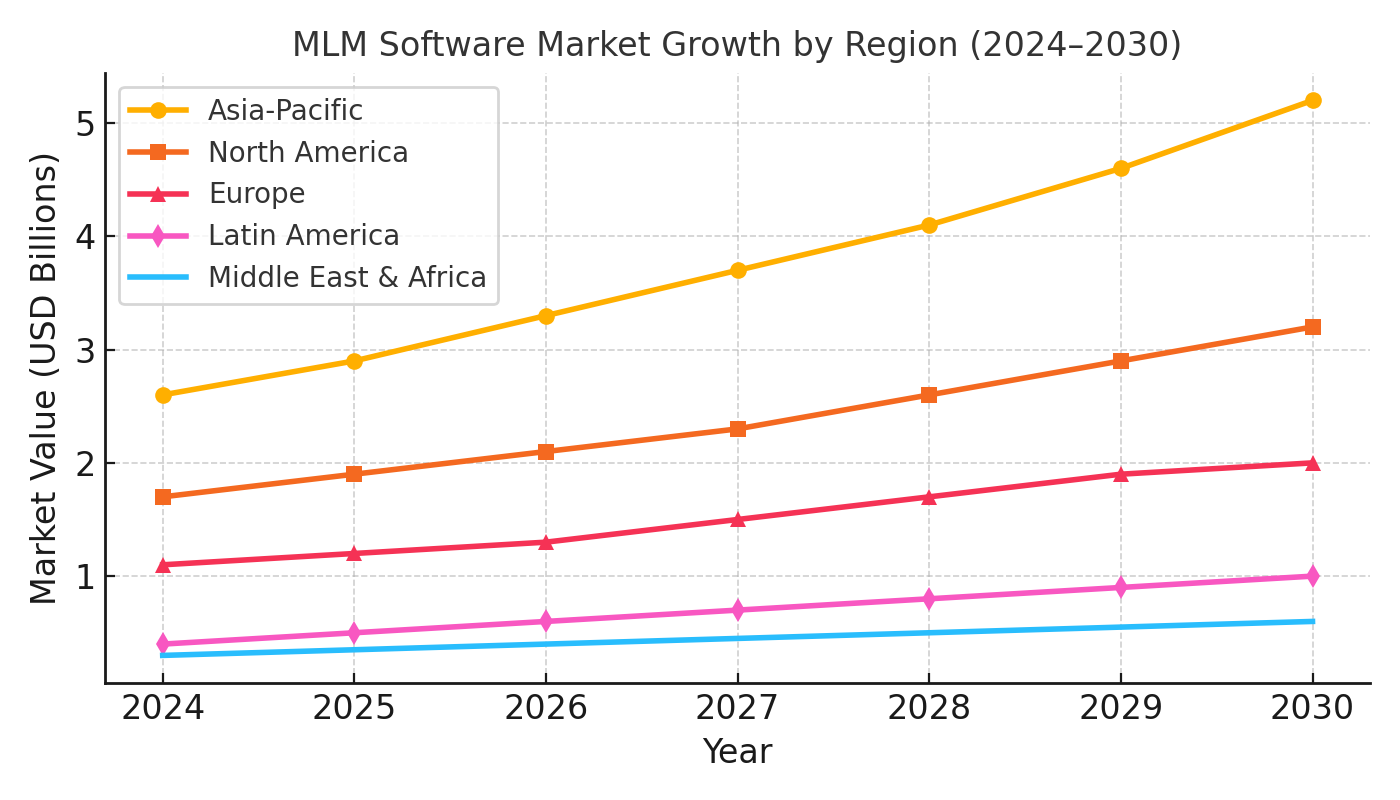
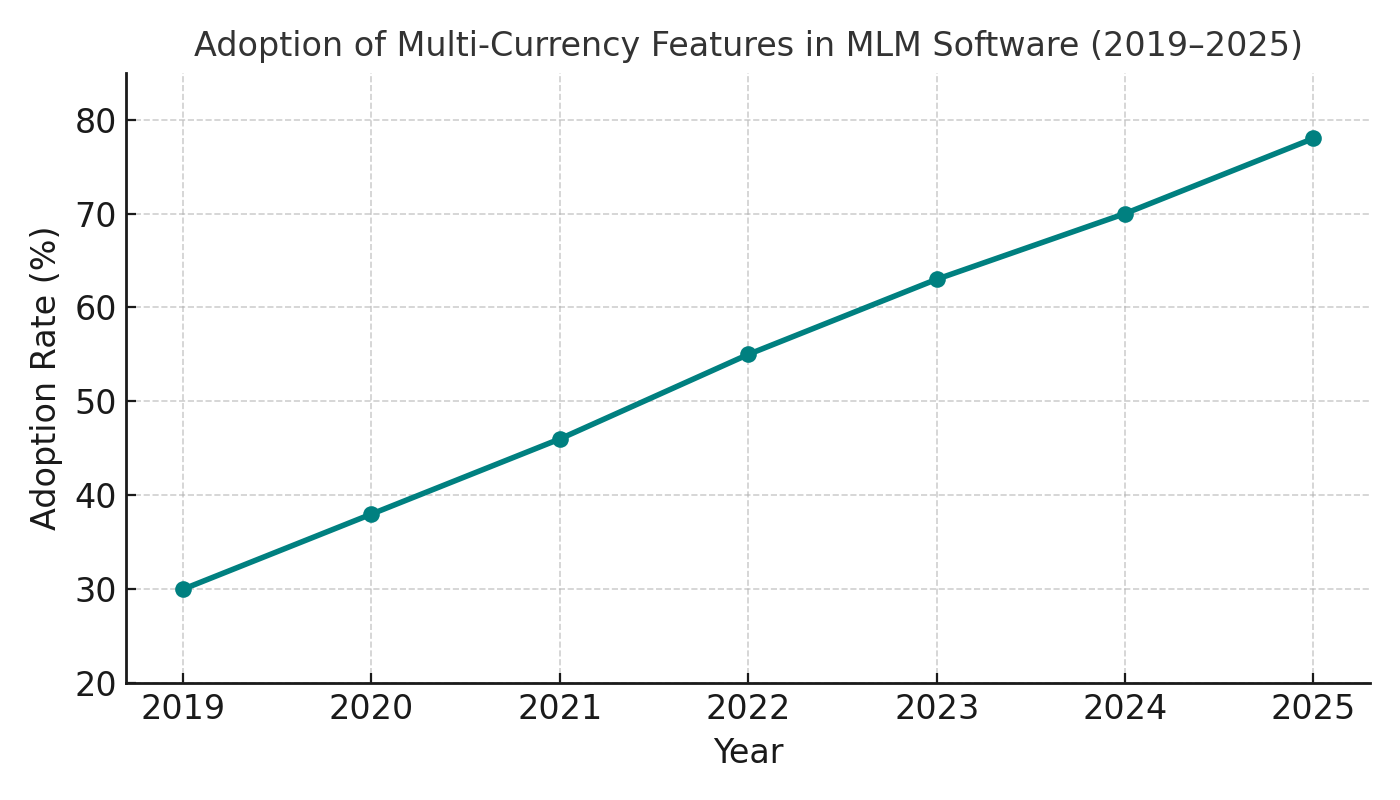
Answer: Internationalization in MLM software refers to designing systems that can adapt to different countries’ currencies, languages, tax regulations, and compliance rules, ensuring smooth cross-border distributor and customer operations.
Answer: Multi-currency support allows distributors and customers to transact in their local currency, reducing payment friction, increasing trust, and improving global sales conversions.
Answer: Supporting multiple languages ensures that distributors and customers can interact with the platform in their native language, boosting engagement, adoption, and compliance with consumer protection regulations.
Answer: Regional catalogs are country-specific product listings that ensure only approved and compliant products are available for sale in each market, based on local regulations and consumer preferences.
Answer: Modern MLM platforms integrate tax profiles that automatically apply local VAT, GST, or withholding tax rules, ensuring compliance and preventing penalties in global markets.
Answer: Fulfillment rules define how orders are processed, shipped, and delivered in different countries, often integrating with regional warehouses, 3PL providers, and local delivery services to reduce delays and costs.
Answer: Key trends include AI-driven localization, blockchain for tax compliance, mobile-first dashboards for distributors, crypto and e-wallet payments, and sustainability-focused supply chain tracking.
As MLM companies expand globally, internationalization is no longer optional—it’s survival. Software that seamlessly handles multi-currency payments, multilingual interfaces, dynamic tax profiles, region-specific catalogs, and adaptive fulfillment empowers businesses to compete in the diverse regulatory and consumer landscapes of 2025.
The winners in the next decade will be MLM firms that view software not just as an administrative tool, but as a strategic enabler of cross-border trust, compliance, and growth.