
Multi-Level Marketing (MLM) has historically relied on centralized payment gateways, manual payouts, and trust-based commission accounting. But as blockchain and crypto payments mature, a new wave of Crypto-MLM platforms is emerging — leveraging transparency, automation, and global reach.
| Metric | Value | Details | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crypto Payment Gateway Market Growth (2024–2025) | $1.69B → $2.0B | Approx. 18.9% CAGR driven by increasing adoption of crypto payment gateways | The Business Research Company |
| Crypto Payment Apps Market Size (2024) | $556.9 Million | Market estimate with exponential growth expected by 2033 | Yahoo Finance |
| Crypto MLM Platforms with Real-Time Audits | Over 65% | New platforms include audit features to reduce disputes and improve transparency | Intel Market Research |
Yet adoption is still nascent. Many network marketers and platform owners are uncertain about how to build a robust architecture or whether crypto integration is worth the added complexity.
| Part | Focus |
|---|---|
| Part 1 | Architecture & How It Works |
| Part 2 | Adoption, Use Cases & Trends |
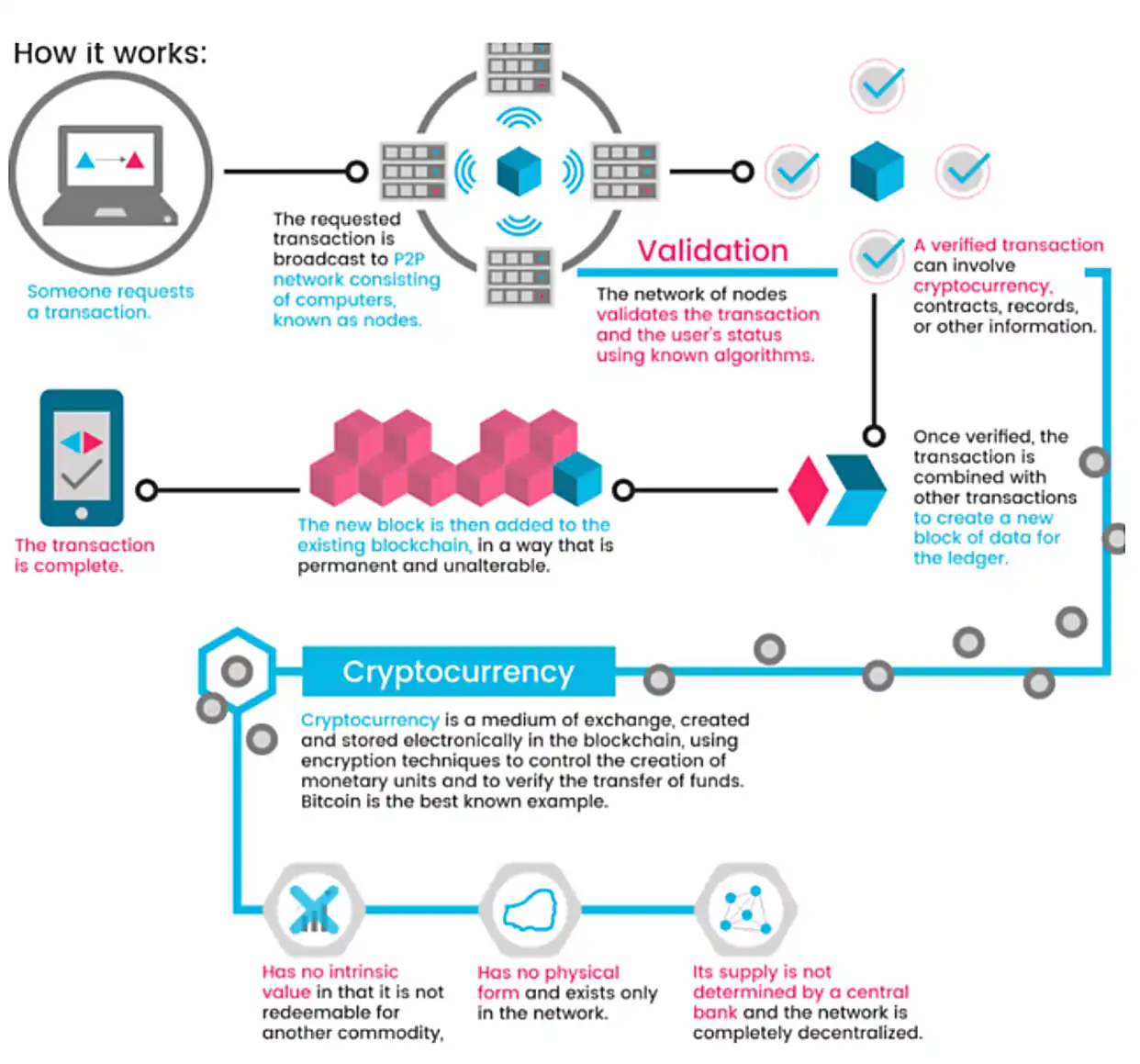
To embed cryptocurrency payments into an MLM platform, you need a layered architecture combining blockchain, smart contracts, off-chain services, wallets, and integration middleware. Below is a conceptual architecture:
| Layer | Function / Role | Design Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain / Ledger Layer | The authoritative record of token transfers, commission events, and reward flows. | Choose between public chains (Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, Solana) or permissioned/consortium blockchains (e.g. Hyperledger Fabric) depending on trust, scale, regulatory, and cost tradeoffs. |
| Smart Contract / Commission Engine | Encodes the MLM compensation rules (binary, matrix, unilevel, hybrid) and automates payouts. | Must be auditable, upgradeable (via proxy or modular design), gas-efficient, and resistant to abuse (reentrancy, overflow). |
| Wallet & Custodial Layer | Interface for users to hold, deposit, withdraw, and display token balances. | Non-custodial (user holds keys) is more trustless but harder for onboarding; custodial (platform holds keys) is easier but increases risk. |
| Payment Gateway / Orchestration | Converts fiat or crypto inputs, routes transactions, handles fees, and reconciles on-chain and off-chain flows. | Could integrate external crypto gateway APIs (e.g. MoonPay, etc.), or build own “crypto gateway” module. |
| Off-chain Services & Oracles | Provide exchange rates, identity checks, and bridging data from external systems. | Use oracles (e.g. Chainlink) for reliable price feeds, KYC/AML modules, compliance checks. |
| Dashboard / Admin / Analytics | For platform operators and participants to view commissions, metrics, auditing, and reports. | Should present transparency (e.g. traceability of each commission trace in a tree) and reconciliation with on-chain state. |
Performance & Cost Mitigation (Hybrid Approaches)
To improve performance and reduce gas costs, many platforms adopt hybrid off-chain and on-chain architectures:
One academic protocol, PayPlace, proposes a scalable off-chain approach for marketplace payments. In this model, users open a virtual payment channel with an operator, who routes payments to merchants, and only the final settlement is posted on-chain. This approach generalizes well to high-volume platforms such as MLM systems.
A permissioned blockchain model using Hyperledger Fabric is also viable. Fabric supports modular consensus and identity management and has demonstrated throughput exceeding 3,500 transactions per second in benchmark configurations—making it suitable for MLM platforms that require low latency and high performance.
On-chain transaction costs can spike unpredictably.
Mitigate by batching transactions, subsidizing fees, or deploying on low-fee chains
(e.g., Polygon, BNB Smart Chain).
MLM business logic evolves, requiring contract upgrades after deployment.
Use proxy patterns and upgrade-safe architectures with strict access controls.
Smart contracts are vulnerable to common attack vectors.
Apply standard security practices: re-entrancy guards, safe math libraries, and
regular audits.
Commission payouts require reliable liquidity.
Maintain reserve pools, use stablecoins, and design sustainable tokenomics.
MLM combined with crypto may be regulated as securities or pyramid schemes.
Integrate KYC/AML, geofencing, and jurisdiction-aware compliance controls.
Many users are unfamiliar with wallets and private keys.
Abstract blockchain complexity using custodial wallets, guided flows,
and familiar UX patterns.
Even with immutable logs, disputes may still occur.
Provide transparent views, downloadable proofs, and verifiable on-chain logs.
Based on current best practices and community guides:
Define MLM Plan Logic: Decide on compensation structure (binary, unilevel, matrix, hybrid) and write it in modular form.
Select Blockchain / Chain(s): Evaluate tradeoffs of gas cost, throughput, security, ecosystem.
Develop Smart Contracts & Audit: Ensure third-party audit; incorporate upgradability.
Build / Integrate Wallet & Custody Module: To support deposits, withdrawals, and transfers.
Integrate Crypto Payment Gateway: Either by using third-party APIs or custom module to accept crypto / fiat-to-crypto flows.
Oracle & Fee / Price Service Integration: Use stable price feeds for valuation and token conversion.
UI / Dashboard / Analytics: Show real-time commission lineage, dashboards, and reconciliations.
Testing & Staging: Stress test on testnet, simulate commission flows, check edge cases.
Go Live with Soft Launch & Monitoring: Monitor gas cost, slippage, user behavior, error rates.
Ongoing Updates & Governance: Govern contract upgrades, token economics adjustments, patches.
However, limitations persist: many users still prefer fiat payouts, regulatory constraints in certain jurisdictions limit pure crypto payouts, and UX friction is real.
Thus, the opportunity is real, but success depends on execution, compliance, and user experience.
| Risk | Description | Mitigation / Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Some countries may view crypto-MLM as pyramid or securities. | Consult legal counsel; implement KYC/AML, licensing, and transparent token economics. |
| Volatility & Token Risk | Crypto tokens fluctuate; users may see commission value erode. | Use stablecoins or hedging, reserve buffers, or hybrid value models. |
| Smart Contract Bugs / Security | Vulnerabilities can lead to fund loss or exploit. | Use professional audits, formal verification, and upgradeable safe modules. |
| Scalability & Gas Spikes | High volume or network congestion can push costs too high. | Use L2, batching, off-chain mechanisms, or sidechains. |
| User Experience / Adoption Friction | Many users unfamiliar with crypto wallets. | Offer custodial wallets initially, clear UI abstractions, tutorials, onboarding support. |
| Liquidity & Funding | Commission payouts depend on available crypto liquidity. | Maintain reserve pools, dynamic funding model, or fiat bridges. |
| Trust & Brand Reputation | Crypto scams are common; MLM is historically sensitive. | Be transparent, provide audit proof, engage third parties, educate participants. |
👉 Try the official MLM Software Demo for Your MLM Business
and experience what MLM Software looks like when it’s powered by the best.
💌 Or, check out our blog
to compare top direct-selling companies, get insider reviews, and learn how to grow your income ethically in the wellness niche.
If you’re building or marketing an MLM platform and considering crypto payments, here’s a strategic to-do list:
In the intersection of MLM + crypto, the promise is converting a trust-based, opaque model into a transparent, automated, high-integrity network. But it’s complex — success depends on rigorous architecture, user-first design, and regulatory compliance.
A1: Cryptocurrency payments in MLM platforms refer to using digital currencies (like Bitcoin, Ethereum or stablecoins) for membership fees, product purchases, and commission payouts. These can be managed through smart contracts to ensure transparency, immutability, and automation.
A2: Smart contracts automate and enforce the MLM compensation logic (binary, matrix, unilevel, etc.). Once preconditions (e.g. referrals, sales) are met, the contract triggers payouts automatically. This reduces delays, human errors, and increases trust among participants.
A3: Key risks include token volatility, regulatory uncertainty (some jurisdictions treat MLM + crypto as securities or ban certain models), smart contract bugs or exploits, user experience friction, and compliance (KYC/AML). Mitigation involves stablecoins, audits, strong compliance programs, good UX design.
A4: Stablecoins (USDT, USDC) are often preferred as they reduce volatility risk. Other choices include major blockchains with low fees (e.g. Binance Smart Chain, Polygon) or custom tokens if the platform has tokenomics in place. The trade-off is between decentralization, cost, speed, and regulatory ease.
A5: Steps include selecting a blockchain (or multi-chain), writing and auditing smart contracts for commission logic, integrating a crypto wallet (custodial or non-custodial), integrating payment gateways or fiat-to-crypto conversion if needed, building dashboards for users/admins, and ensuring compliance and support for user onboarding.