

Cryptocurrency MLM is a business model that combines elements of pyramid schemes with digital currencies. Participants earn money not only through their own investments and sales of crypto-related products but also by recruiting new members into the scheme, forming a downline from which they receive commissions. Often disguised as legitimate investment opportunities, these structures heavily rely on continuous recruitment to pay off earlier investors, making them inherently unsustainable and highly risky.
The rise of blockchain technology has created new business models that blend traditional multi-level marketing (MLM) with cryptocurrency tokens. Promoters often promise high returns, instant payouts, and global scalability. However, behind the flashy dashboards and token incentives lie serious risks—including custody issues, volatility, and regulatory scrutiny. In this article, we will unpack the real-world risks of crypto/token-based MLM schemes and explore controls, red flags, and safer alternatives for investors and participants.
One of the biggest appeals of crypto-based MLMs is instant global payouts. Instead of waiting weeks for commissions, tokens can be transferred within minutes. However, this speed introduces two major risks: custody and volatility.
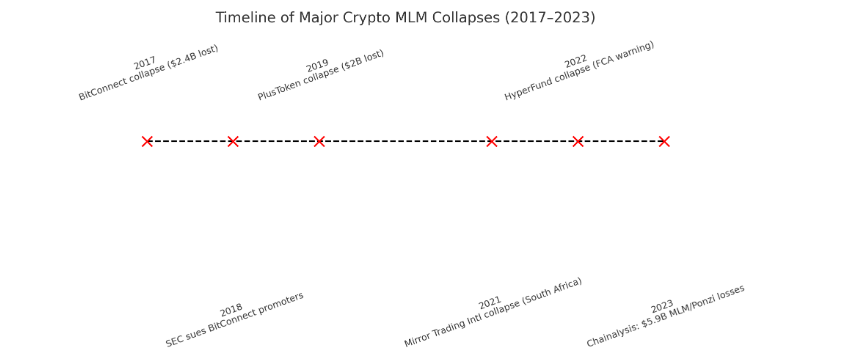
Unlike regulated brokers or banks, most MLMs lack licensed custodians. Instead, they hold user funds in centralized wallets controlled by the company. History has shown how vulnerable this setup is:
With no regulatory oversight, participants have no recourse if funds disappear.
Most MLMs pay commissions in their native token or volatile cryptocurrencies. Unlike fiat, these assets can swing dramatically. For example:
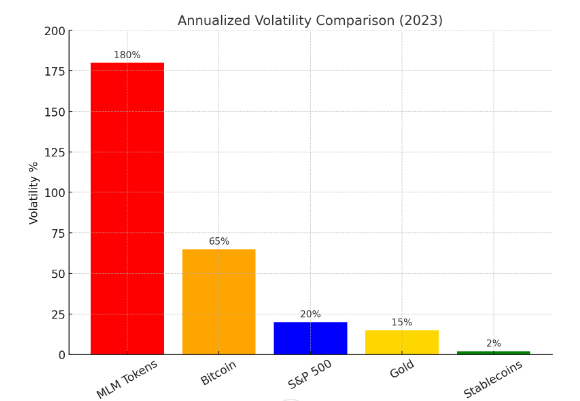
This volatility creates a mismatch between promised payouts and actual realized value. A $500 commission in January could be worth less than $200 by March if token prices collapse.
Governments worldwide are intensifying scrutiny of token-based MLMs, often categorizing them as unregistered securities or outright Ponzi schemes.
Rather than risky token-based MLMs, participants can explore regulated models of digital finance:
The post-2022 crypto winter accelerated scrutiny of token MLMs. Several global reports highlight this shift:
Meanwhile, legitimate blockchain adoption is thriving:
Let’s visualize the risk-reward gap of token-based MLMs vs. regulated alternatives:
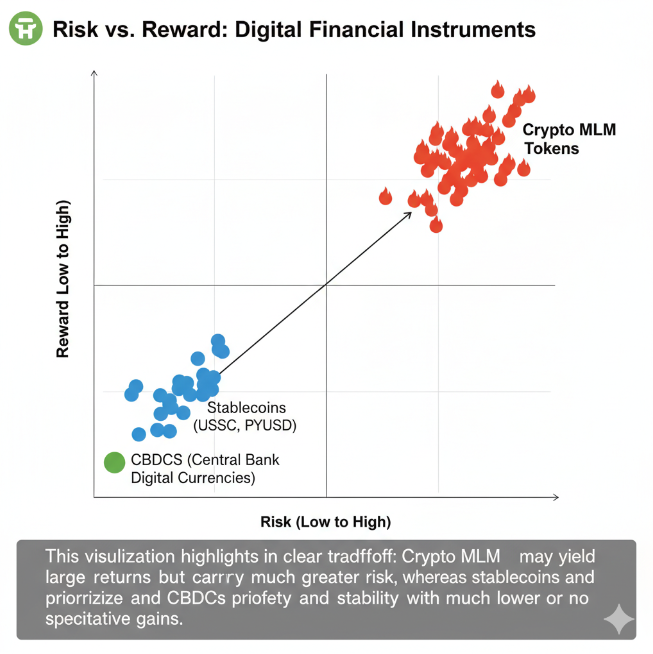
Crypto/token-based MLMs remain one of the riskiest intersections of blockchain and finance. While their promise of fast payouts and borderless opportunities appeals to many, the custody vulnerabilities, token volatility, and regulatory red flags make them unsustainable for long-term participants.
Instead of chasing quick gains through unregulated MLM schemes, individuals should prioritize regulated, transparent, and liquid financial tools like stablecoins, CBDCs, and tokenized loyalty programs. The future of blockchain lies not in MLM-style token pyramids, but in sustainable and compliant adoption that protects participants.
Always apply the “regulator’s lens”—if an opportunity promises high returns with little explanation of risk, it’s not innovation, it’s exploitation.
Not all crypto MLMs are illegal by default, but most operate in a regulatory gray zone. If an MLM relies primarily on recruitment and promises guaranteed returns, regulators like the SEC (U.S.), FCA (U.K.), and SEBI (India) classify it as a pyramid scheme and pursue enforcement actions. Always check whether the platform has proper financial licenses.
The two main risks are custody (loss of funds due to scams or hacks) and volatility (crypto token values dropping drastically). Many MLM tokens lose 90–99% of their value within a year, making payouts effectively worthless.
Red flags include:
Safer options include:
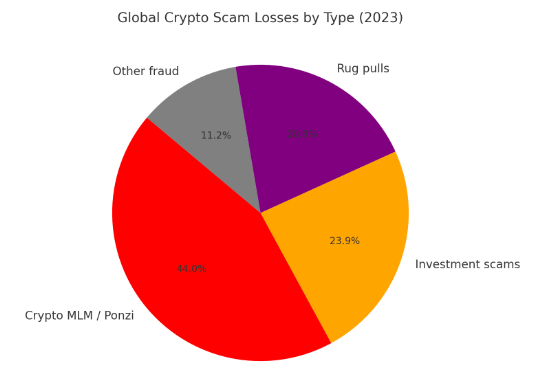
According to Chainalysis (2023), crypto Ponzi and MLM scams accounted for $5.9 billion in global losses in 2023 alone—the single largest category of fraud in the crypto industry.
Read in Detail about :