
Shopify MLM integration is the process of connecting Shopify’s e-commerce platform with multi-level marketing (MLM) software so that businesses can manage sales, downlines, commissions, and affiliate networks directly within their online store. While Shopify powers product catalogs, payments, and customer orders, MLM integration adds layers of genealogy tracking, commission rules, and distributor management. Achieving this requires APIs, extensibility models, and event-driven workflows that ensure data flows securely and consistently between Shopify and the MLM engine.
In today’s hyper-connected E-commerce ecosystem, businesses increasingly rely on integrating multi-level marketing (MLM) software with Shopify to scale operations, improve affiliate workflows, and streamline customer experiences. But while Shopify provides a powerful commerce backbone, extending it with MLM logic requires APIs, extensibility models, and careful handling of event-driven architectures.
In this guide, we’ll explore the reference architecture for Shopify + MLM integration, focusing on webhooks, idempotency keys, and APIs to ensure reliable, scalable, and fault-tolerant operations.
Traditional eCommerce platforms are transaction-centric—focused on orders, carts, payments, and fulfillment. MLM models, however, introduce network-centric logic such as:
By integrating MLM software with Shopify, businesses unlock:
✅ Seamless tracking of downline sales
✅ Real-time commission automation
✅ Improved user onboarding for affiliates
✅ Customizable payout cycles
But here’s the challenge: Shopify isn’t natively built for MLM logic. This is where APIs, webhooks, and extensibility principles come into play.
Here’s a high-level architecture diagram for Shopify + MLM extensibility:
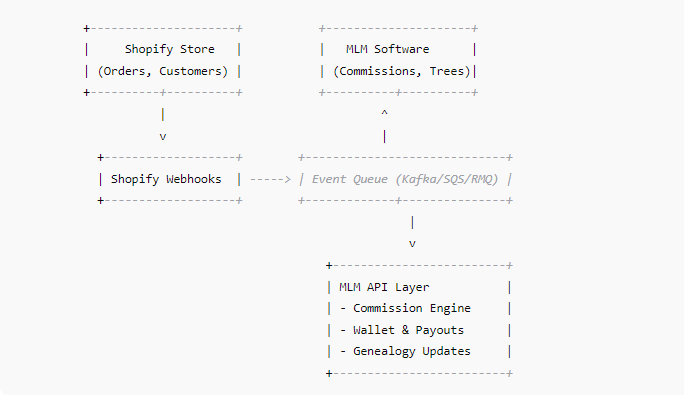
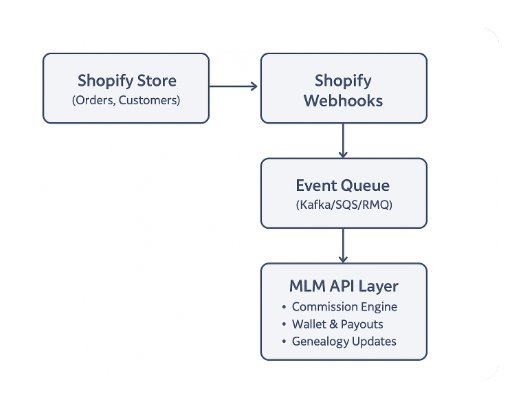
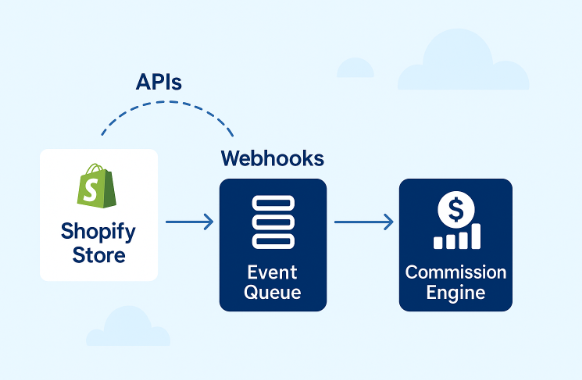
1. Shopify Webhooks
orders/create or customers/update.Example Payload (simplified):
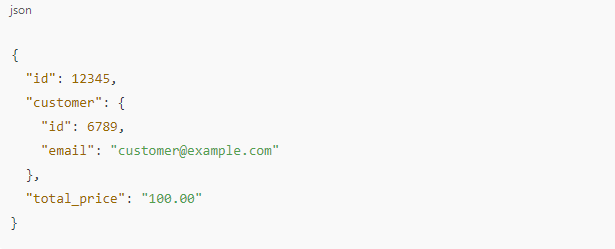
👉 This data is enriched with MLM logic to identify
who referred the customer and
how commissions should be split.
2. Event Queue for Reliability
3. MLM API Layer
This is the heart of MLM extensibility. Key microservices include:
Each service should expose idempotent REST APIs (using tokens/keys) to prevent duplication.
4. Idempotency Keys for Safe Transactions
Why are they needed? Because Shopify webhooks retry multiple times until acknowledged. Without safeguards, you may:
❌ Duplicate commissions
❌ Over-credit wallets
❌ Break genealogy hierarchies
Solution: Use idempotency keys—unique identifiers for each transaction.
Example:
#12345idempotency_key=12345| Shopify Event | MLM Action Triggered | Example Workflow |
|---|---|---|
orders/create |
Commission calculation | Affiliate gets % of referral sale |
orders/refund |
Reverse commission | Deduct previously credited commission |
customers/create |
Add user to genealogy tree | Customer linked under sponsor’s downline |
payouts/initiate |
Wallet → Bank Transfer | Scheduled commission payout to affiliate |
products/update |
MLM rank/bonus recalculation | Special bonuses for certain product sales |
orders/create webhook.
Building a Shopify + MLM extensibility architecture is more than just plugging in APIs — it requires
robust event handling, careful idempotency management, and scalable design patterns.
With webhooks triggering MLM workflows, idempotency keys preventing duplication, and APIs enabling modular extensibility,
businesses can confidently grow affiliate-driven sales without compromising reliability.
The future of eCommerce lies in ecosystems, not silos. By connecting Shopify with MLM software, you’re not just selling products — you’re empowering networks.
✅ Pro Tip for Implementation: Always start with a
sandbox store and staging MLM environment. Test idempotency handling extensively before going live 👉