

MLM for digital products and services is a business model where a multi-level marketing company sells non-physical goods such as software subscriptions, online courses, cloud storage, or consulting services through a network of independent distributors. Unlike traditional MLM focused on physical products, this model leverages the internet’s scalability to offer products with no inventory or shipping costs. This makes the business highly attractive due to its low overhead, global reach, and the ability to offer a diverse and rapidly-evolving portfolio of digital solutions.
Multilevel marketing has long been associated with physical goods — cosmetics, supplements, kitchenware — but the rise of digital products and services (courses, SaaS, memberships, APIs, digital media) is shifting that landscape. This article explores how MLM-style distribution can work for intangible offerings, and digs into two crucial subtopics:
1) Subscriptions & usage-based commissions and
2) Compliance for non-tangible products.
It uses current market benchmarks and regulatory guidance so operators and affiliates can make evidence-backed decisions.
Whop,
Zuora,
DemandSage,
TheModeler.com, and
Federal Trade Commission
provide valuable resources.
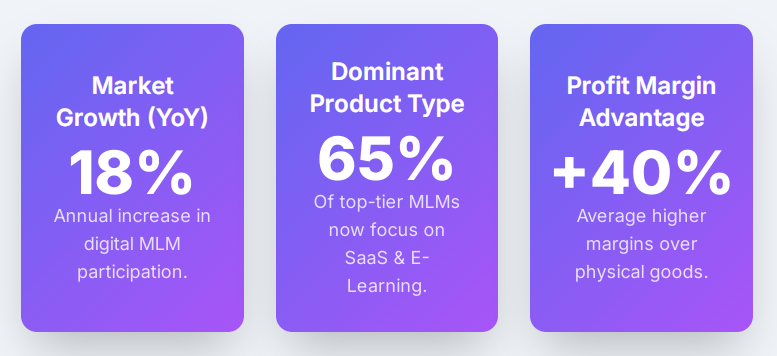
Digital products are massive and growing. Estimates put the annual economic value created by digital products at roughly $2.5 trillion in 2025, driven by subscriptions, digital media, and software monetization. The broader digital media market alone was about $833 billion in 2023 and still expanding. That scale makes digital goods attractive to direct-selling networks that need high-margin, instantly deliverable inventory.
Whop,
Grand View Research
provide valuable insights.
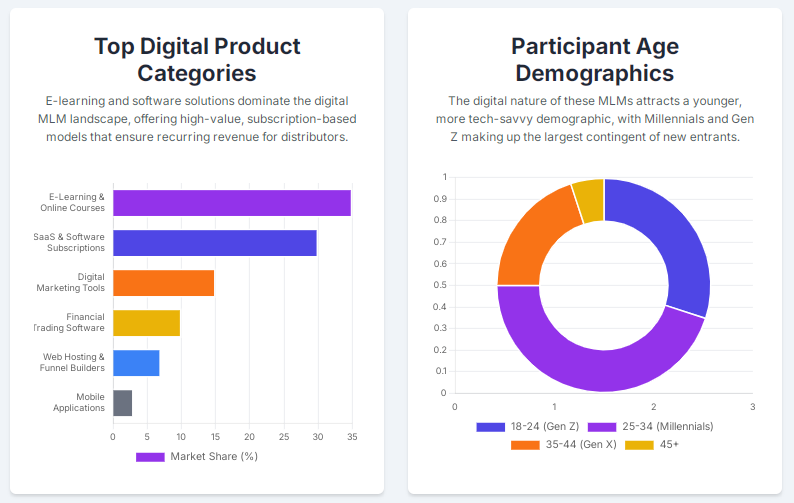
Two quick benchmarks to keep in mind (visualized in the charts I generated above): Zuora’s Subscription Economy Index finds subscription-based companies outperforming peers (SEI companies saw roughly 11% faster revenue growth than the S&P over recent two-year windows), and affiliate/partner models drive about 16% of U.S. online orders, demonstrating the potency of performance-based sales channels. These numbers frame why combining MLM incentive structures with digital distribution can be powerful — when done right.
Zuora,
DemandSage
offer further data.
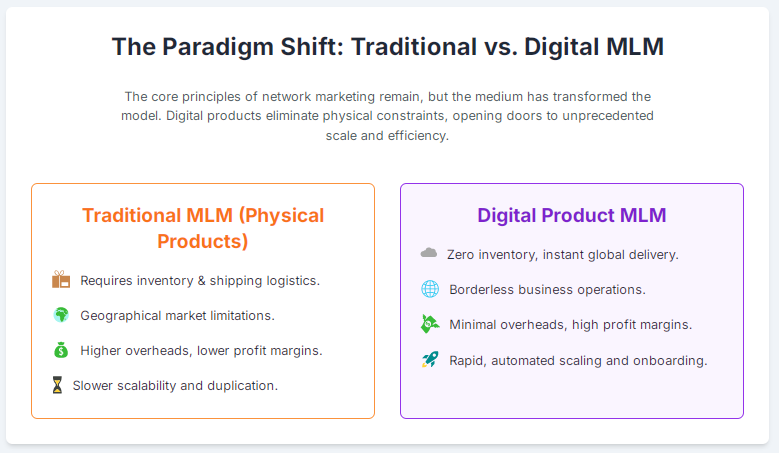
Moving from one-time digital purchases to recurring revenue is natural for digital goods. Recurring models also map well to MLM-style residual compensation — but they require thoughtful plan design.
Models that work
Benchmarks & economics
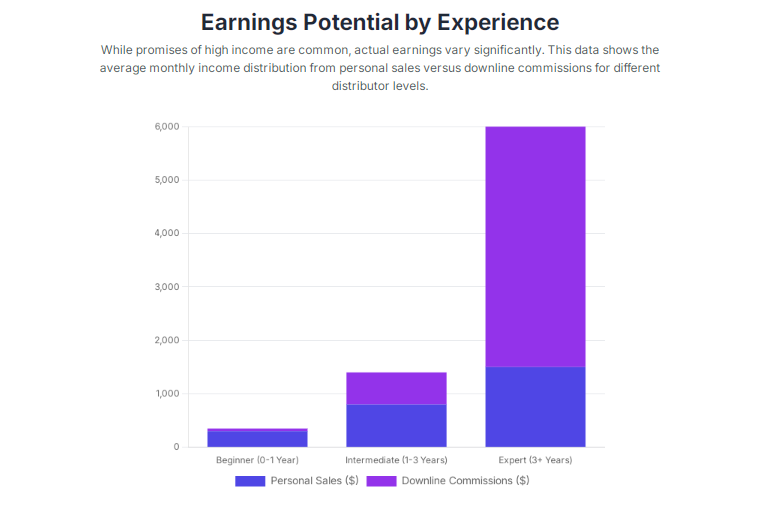
Important metrics to track
Practical design rules
Digital products bring unique legal and reputational issues for MLMs: intangible delivery, free trials, auto-renewals, and influencer endorsements. Compliance is not optional — regulators have scrutinized recruitment-focused plans and misleading earnings claims for years.
Advertising & endorsement law
U.S. guidance from the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) requires truth-in-advertising and transparent endorsement disclosures. When network sellers recommend a subscription or digital product and receive payment (or compensation tied to sales), that relationship must be clearly disclosed. The FTC revised its Endorsement Guides to reflect social media and new channels; failure to disclose can lead to enforcement action and reputational harm. Simple disclosures (e.g., “I get paid if you sign up”) must be clear and unavoidable.
Federal Trade Commission
Consumer protection (auto-renew, refunds)
Many jurisdictions require clear disclosure of auto-renewal terms, easy cancellation, and accessible refund policies for digital subscriptions. EU consumers have strong rights under consumer protection directives and GDPR affects data handling for digital services. Practical steps:
MLM-specific scrutiny
Regulators and NGOs scrutinize MLMs that prioritize recruitment over product sales. If a program rewards recruitment disproportionately and sellers mainly buy the product themselves rather than sell to external customers, it risks being classified as an illegal pyramid scheme in many jurisdictions. For digital products — which are cheaper to obtain and easier for sellers to consume themselves — the risk profile can be higher. To mitigate:
Privacy & data security
Digital products collect personal data. GDPR (EU), CCPA/CPRA (California), and other privacy laws impose data subject rights and security obligations. Ensure:
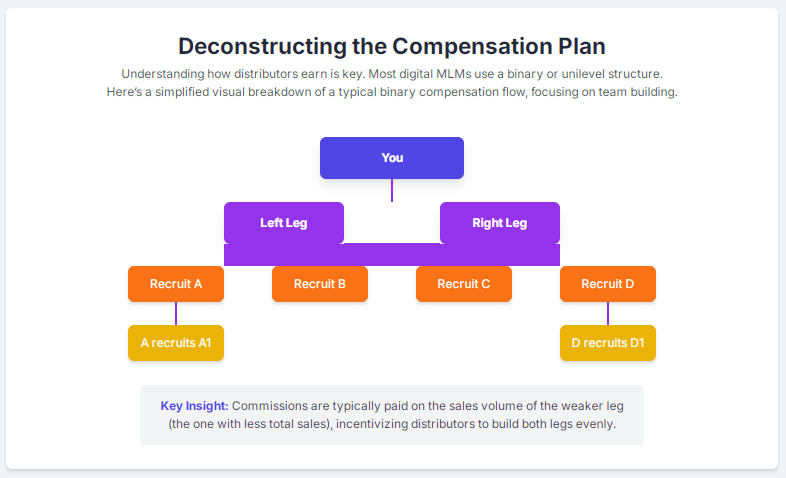
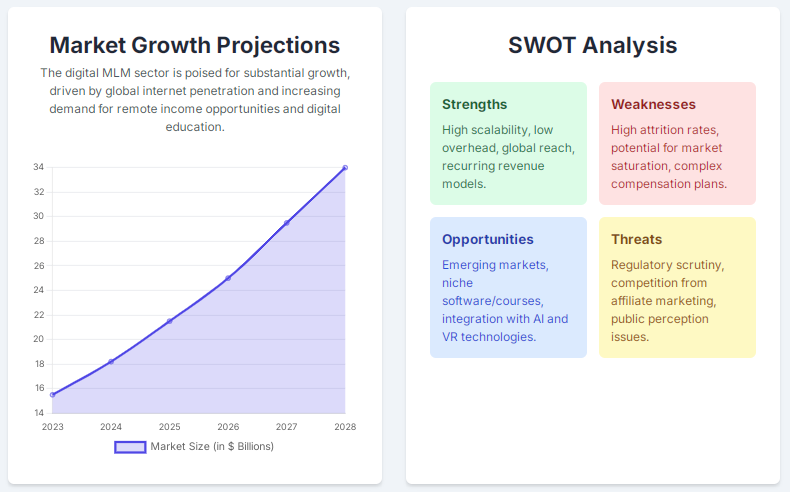
MLM for digital products and services can unlock enormous reach and low-friction distribution: the total addressable opportunity is measured in the trillions, subscriptions deliver predictable recurring revenue (and stronger valuation multiples), and affiliate/partner performance channels already drive a meaningful slice of online commerce. But scale responsibly: design commission plans that reflect margins and retention, and obey advertising, consumer-protection, and privacy obligations to avoid legal and reputational risk. When done right, the blend of performance-based distribution plus recurring digital monetization creates a resilient, modern alternative to classic product-based MLM.
Know more @